- 3/11/19 9:23 AM
- David Modrego

CHEOPS mission consists of the satellite, also named CHEOPS, a control center named MOC (Mission Operations Center), two tracking centers where the antennas are located with which we communicate with the satellite and a scientific operations center named SOC (Science Operations Center).
The mission is developed as a collaboration between ESA and the Swiss Space Agency, with important contributions from several European countries, including Spain, which builds both the satellite (Airbus Spain) and the control center (GMV). Switzerland is responsible for the construction and planning of the use of the instrument and the processing of the data it generates.
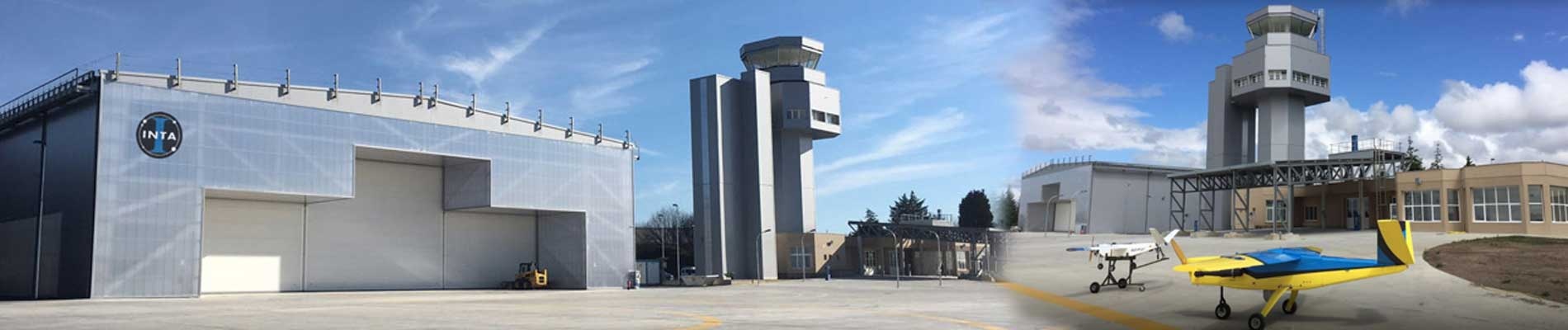
INTA has an important role in this mission, being in charge of operating the satellite from the control center (MOC) located in the Space Center INTA Torrejón (CEIT) from which the entire operation of the satellite will be commanded and also puts the monitoring centers of Torrejón and Villafranca. INTA will be responsible from the execution of LEOP (Launch and Early Orbit Phase).
CEIT hosts the MOC of CHEOPS
From CEIT the orders will be sent to the satellite and it will be received the telemetry data transmitted by the satellite. It will be needed to check the state of the satellite, respond to any anomaly, calculate where the satellite is and when it will happen again over us ...
Within the CEIT there are a lot of servers, computers and applications that help us do all these operations. The core of them all is the MCS (Mission Control Center). The MCS is the tool in which we can choose the commands that we want to send to the satellite and where we see the satellite responses.
MCS application windows
Furthermore, there are other systems, as FDS, GFTS,… we even have a satellite simulator! Each one has its objective, you will see ...